Cryogenic air separation is a widely used industrial process to produce high-purity oxygen, nitrogen, and other gases by cooling atmospheric air to extremely low temperatures. This technique takes advantage of the differing boiling points of air’s main components (oxygen at –183°C, nitrogen at –196°C, and argon at –186°C) to achieve separation through fractional distillation. Cryogenic Air Separation Units (ASUs) compress, purify, and cool air before channeling it into cryogenic distillation columns, where the gases are recovered at high purity.
Modern Cryogenic Air Separation processes deliver large volumes of pure gases for critical applications in steel production, chemical manufacturing, electronics fabrication, and healthcare. For example, ultra-pure oxygen is needed in steelmaking, high-purity nitrogen is used for semiconductor manufacturing and food processing, and pure argon serves as a protective inert gas in welding and pharmaceutical processes. As global demand for industrial gases grows, advanced Cryogenic Air Separation technology provides an efficient and reliable way to produce these gases at scale.

Principles of Cryogenic Air Separation
Cryogenic air separation uses fractional distillation of liquefied air to isolate its components. Compressed and purified air is cooled to cryogenic temperatures (around –185°C) so that some of it condenses into liquid form. This cold liquid–vapor mixture is fed into a vertical distillation column. Because oxygen, nitrogen, and argon have different boiling points, they boil off at different heights in the column. Nitrogen (–196°C boiling) emerges as vapor at the top, while oxygen (–183°C) collects as liquid at the bottom. Argon (–186°C) is extracted from an intermediate point if needed. By carefully maintaining temperature and pressure gradients inside the column, the ASU yields very pure nitrogen, oxygen, and argon streams without chemical additives.
Process Flow of a Cryogenic Air Separation Unit (ASU)
A cryogenic ASU operates in sequential stages to transform air into pure gases:
- Compression: Ambient air is drawn in and compressed (typically to 6–8 bar). This high-pressure air is the starting point for efficient cooling and separation.
- Purification: The compressed air is passed through filters and molecular sieve beds to remove moisture, CO₂, and other impurities. This purification is essential to prevent ice or solid deposits in downstream equipment.
- Cooling and Liquefaction: Purified air flows through main heat exchangers, where it is progressively cooled by cold product streams and an expansion refrigerant. Eventually the air reaches cryogenic temperature and partially liquefies.
- Distillation: The cold mixture enters one or more distillation columns inside a coldbox. In a typical two-column setup, a high-pressure column first separates bulk nitrogen and oxygen, and a low-pressure column further refines purity. Nitrogen gas exits the top, while liquid oxygen (and argon, if any) is drawn from lower sections.
- Product Collection: Separated gases are collected. Nitrogen and oxygen are reheated and sent to storage or users; any liquid oxygen or nitrogen is collected in cryogenic tanks. Byproducts like argon are recovered via additional columns if required.
Key Components and Equipment
Cryogenic ASUs are built from specialized equipment. Key components include:
- Compressors: Multi-stage compressors pressurize air to around 6–8 bar, which improves the efficiency of cooling and separation stages.
- Purification Beds: Filters and molecular sieves remove moisture, CO₂, and hydrocarbons from the compressed air. This purification is essential to prevent freezing and fouling in the cryogenic heat exchangers.
- Main Heat Exchangers (Coldbox): High-efficiency plate-fin heat exchangers cool the purified air by exchanging heat with outgoing cold gases and liquids. The coldbox contains these exchangers and the distillation columns in one insulated enclosure.
- Expander/Refrigeration Turbine: A portion of the high-pressure nitrogen is routed through an expansion turbine, which provides a cold refrigeration stream to help liquefy the incoming air.
- Distillation Columns: Typically arranged as a high-pressure column followed by a low-pressure column, these separate the liquefied air. Pure nitrogen emerges from the top of the second column, and high-purity oxygen is drawn from the bottom. An auxiliary column may recover argon if required.
- Product Tanks: The separated nitrogen and oxygen gases are warmed and sent to pressurized storage or pipelines. Any liquid products are collected in cryogenic storage tanks for transport or use as needed.
- Control and Safety Systems: Modern ASUs use PLC-based control systems with operator interfaces to monitor pressures, temperatures, and flows. Automated controls regulate valves and compressors for stable operation and include safety interlocks to protect the equipment.
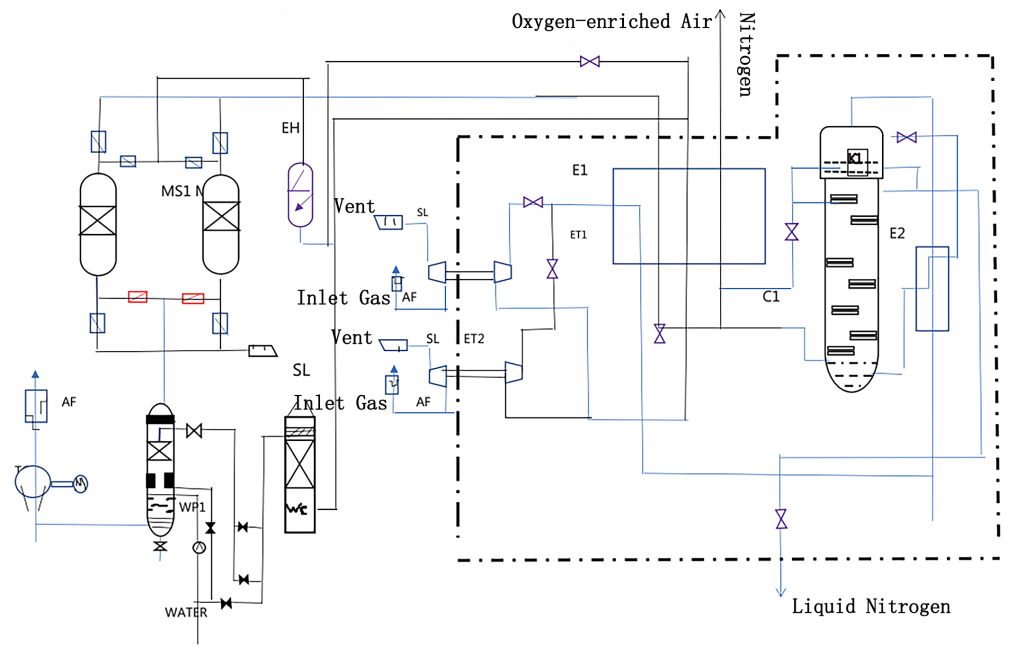
Performance and Efficiency
Key performance metrics for cryogenic air separation include product purity, output capacity, and efficiency. Cryogenic ASUs can produce ultra-high purity gases: nitrogen streams often have oxygen levels below 10 ppm, and oxygen products exceed 99.5% purity. Designed for continuous operation, these units provide stable flow rates under varying conditions.
- Product Purity: Cryogenic ASUs reliably yield industrial gases at very high purity. Typical products include nitrogen (<10 ppm O₂) and oxygen (>99.5%), meeting the requirements for semiconductor, medical, and specialty gas applications.
- Efficiency and Air Consumption: Efficiency is measured by the ratio of input air to product output. Advanced ASU designs use integrated heat exchangers and expanders to reduce power use. For example, a mid-size unit may use roughly 3–5 Nm³ of air per Nm³ of nitrogen. Optimized heat exchangers and refrigeration cycles help minimize feed air requirements and energy use.
- Stable Operation: Automated controls and feedback loops maintain constant pressures and temperatures. This ensures steady production even as demand shifts. The reliability of cryogenic systems means downtime is minimal when properly maintained.
- Automation and Control: PLC-based systems provide precise control over the process. Real-time monitoring of flow, pressure, and temperature, along with safety interlocks and alarms, enhance operational reliability and simplify maintenance.
Sheng Er Gas’s Core Advantages
Sheng Er Gas offers advanced cryogenic ASUs with several key strengths:
- Ultra-High Purity: Sheng Er Gas ASUs consistently achieve nitrogen oxygen levels of ≤10 ppm (≤0.001%). Such ultra-low contamination far exceeds many industry requirements, ensuring very pure gas output.
- Optimized Efficiency: Efficient heat exchange and refrigeration design minimize the feed air and energy needed per unit of product. Each system is tuned to deliver maximum gas output per unit of air, keeping operational costs low.
- Stable Continuous Output: The robust design and process control maintain constant pressure and flow. These ASUs handle load changes smoothly, providing uninterrupted gas supply even under varying demand or electrical conditions.
- Advanced PLC Control: Each ASU is equipped with a modern PLC and user-friendly interface for precise automation. Real-time monitoring and automated interlocks ensure safe, reliable operation, while remote diagnostics simplify maintenance.
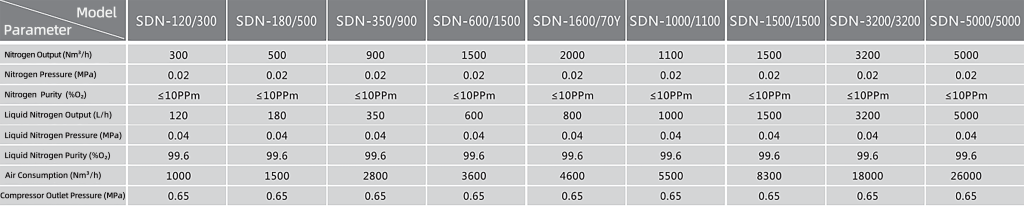
The table below provides sample specifications for several Sheng Er Gas cryogenic ASU models, illustrating typical nitrogen output, purity, pressure, and air consumption.
Table 1. Key specifications for Sheng Er Gas cryogenic ASU models (nitrogen output, purity, pressure, and air consumption).
| Model | N₂ Output (Nm³/h) | Pressure (MPa) | Purity (≤O₂ ppm) | Air Consumption (Nm³/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDN-120/300 | 300 | 0.02 | ≤10 | 1000 |
| SDN-180/500 | 500 | 0.02 | ≤10 | 1500 |
| SDN-350/900 | 900 | 0.02 | ≤10 | 2800 |
| SDN-600/1500 | 1500 | 0.02 | ≤10 | 3600 |
| SDN-1600/2700 | 2000 | 0.02 | ≤10 | 4600 |
| SDN-1000/1100 | 1100 | 0.02 | ≤10 | 5500 |
| SDN-1500/1500 | 1500 | 0.02 | ≤10 | 8300 |
| SDN-3200/3200 | 3200 | 0.02 | ≤10 | 18000 |
| SDN-5000/5000 | 5000 | 0.02 | ≤10 | 26000 |
Industrial Applications
Cryogenic air separation provides oxygen, nitrogen, and argon for many industries:
- Metallurgy and Steelmaking: High-purity oxygen is used in steel furnaces and converters. Nitrogen and argon are used for inerting and cooling in metal processing.
- Chemical and Petrochemical: Processes like ammonia or ethylene production require pure oxygen or nitrogen. Cryogenic nitrogen is also used as an inert gas and as feedstock for chemical reactions.
- Energy and Power: Oxygen-enhanced combustion in power plants increases efficiency and lowers emissions. Nitrogen and argon are used in gas turbines and large engine cooling.
- Electronics and Semiconductor: Ultra-pure nitrogen and oxygen are needed for semiconductor wafer processing and integrated circuit fabrication, where contamination must be strictly controlled.
- Food, Beverage, and Pharma: Nitrogen from ASUs is used for food packaging, beverage dispensing, and inerting, while pure oxygen is supplied to hospitals and clinics for medical use.
- Welding, Fabrication, and Glass: Argon is used in welding and laser cutting as an inert shielding gas. Oxygen is used in cutting and welding torches. Nitrogen and argon also assist in high-quality glass and electronics manufacturing.

Conclusion
Cryogenic air separation remains a mature and highly efficient method for producing industrial gases. By leveraging cryogenic fractional distillation, modern ASUs consistently deliver ultra-pure oxygen and nitrogen with high reliability. Carefully engineered process stages and advanced control systems ensure that each ASU provides stable product flows and meets exacting purity specifications.
Systems like those from Sheng Er Gas incorporate state-of-the-art heat exchange and PLC automation to maximize efficiency. These plants routinely achieve oxygen levels as low as 10 ppm in the nitrogen stream while optimizing air and energy use. The integration of digital controls and remote monitoring further enhances safety and simplifies operation.
As a result, today’s cryogenic ASUs serve critical needs across steel, chemical, energy, electronics, and other industries. Whether supplying a large steel mill or a medical facility, cryogenic air separation units provide a dependable supply of high-purity gases. Sheng Er Gas’s focus on purity, stability, and efficiency ensures that its ASUs meet the rigorous demands of industrial gas customers worldwide.





